Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body produces or uses insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. There are two main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in a lack of insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. This leads to high blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of Diabetes
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
Risk Factors for Diabetes
- Family history
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Age
- Race or ethnicity
- Certain medications
Complications of Diabetes
If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Heart disease
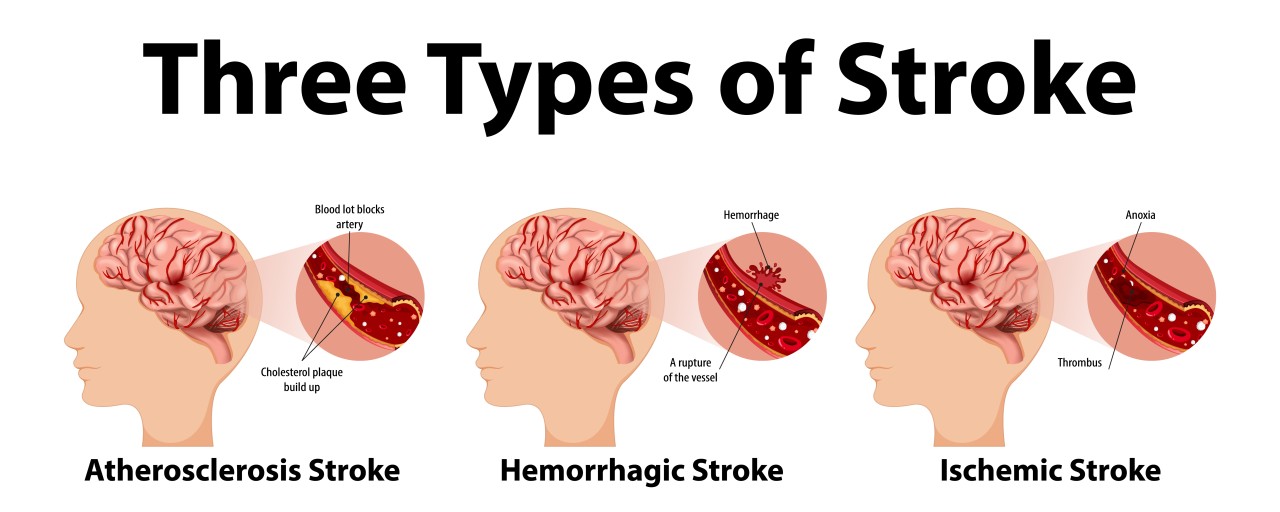
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Nerve damage
- Retinopathy (eye damage)
- Amputation
Managing Diabetes
The management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Medication: People with type 2 diabetes may need to take medication to help control their blood sugar levels. In some cases, people with type 1 diabetes may need to take insulin injections.
- Regular monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. If you have concerns about your risk of diabetes or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to see your doctor for a diagnosis and treatment plan.