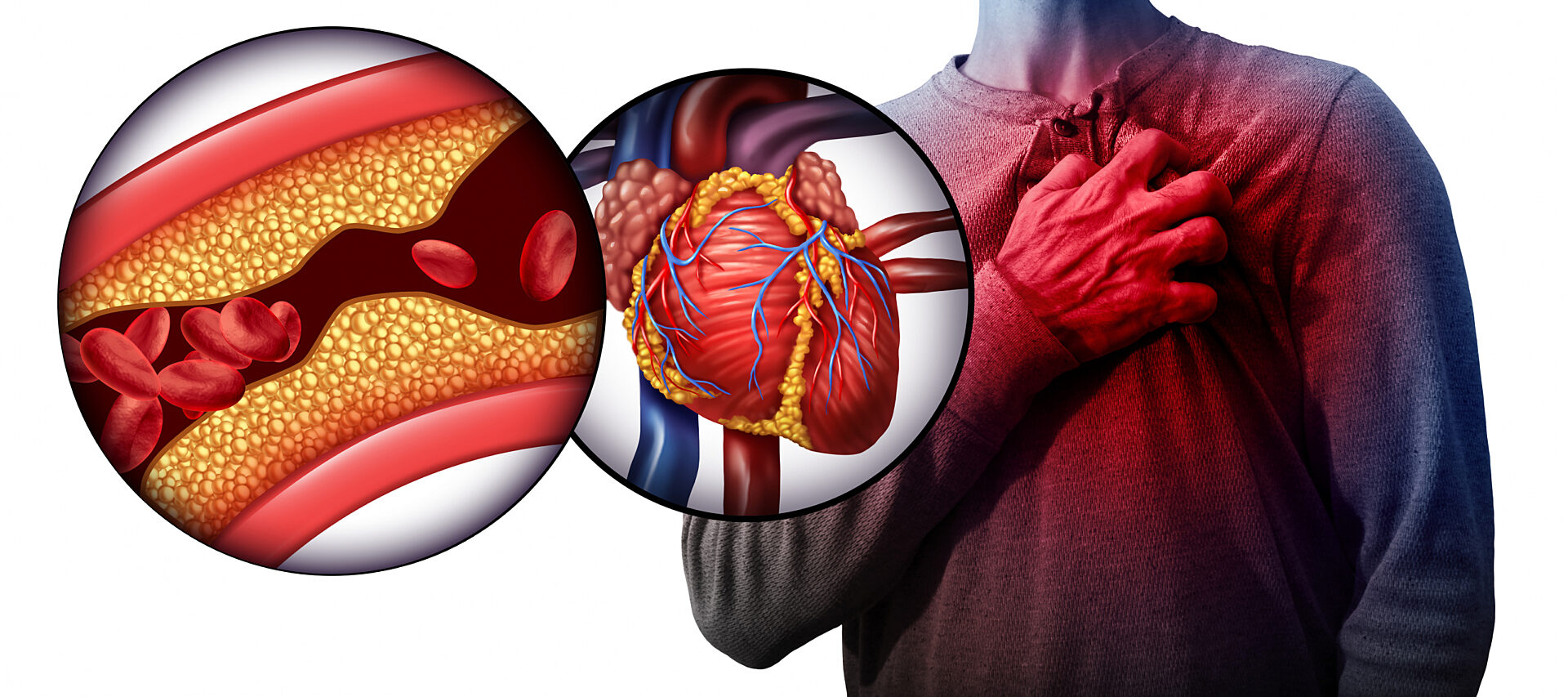
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a section of the heart muscle is blocked. This blockage is typically caused by a blood clot that forms in a coronary artery, which supplies blood to the heart.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
- Chest pain or discomfort: Often described as a squeezing, pressure, fullness, or pain that may spread to the shoulder, arm, neck, jaw, or back.
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fatigue
- Irregular heartbeat
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to call emergency services immediately.
Causes of a Heart Attack
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): The buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries can narrow them, leading to reduced blood flow and an increased risk of clots.
- Blood Clots: These can form in the arteries and block blood flow to the heart.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can damage the arteries and increase the risk of clots.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes have a higher risk of heart disease.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Treatment for a Heart Attack
- Emergency Medical Treatment: Prompt medical intervention is essential to restore blood flow to the heart. This may involve medications, angioplasty (a procedure to open the blocked artery), or bypass surgery.
- Rehabilitation: After a heart attack, rehabilitation programs can help individuals recover and improve their heart health. These programs often include exercise, dietary changes, and stress management techniques.
Prevention of Heart Attacks
- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Quit smoking
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- Balanced diet
- Manage stress
- Medical Management:
- Regular checkups
- Medications (e.g., blood pressure, cholesterol-lowering)
By understanding the risk factors for heart attacks and taking proactive steps to prevent them, you can significantly reduce your chances of experiencing this medical emergency.