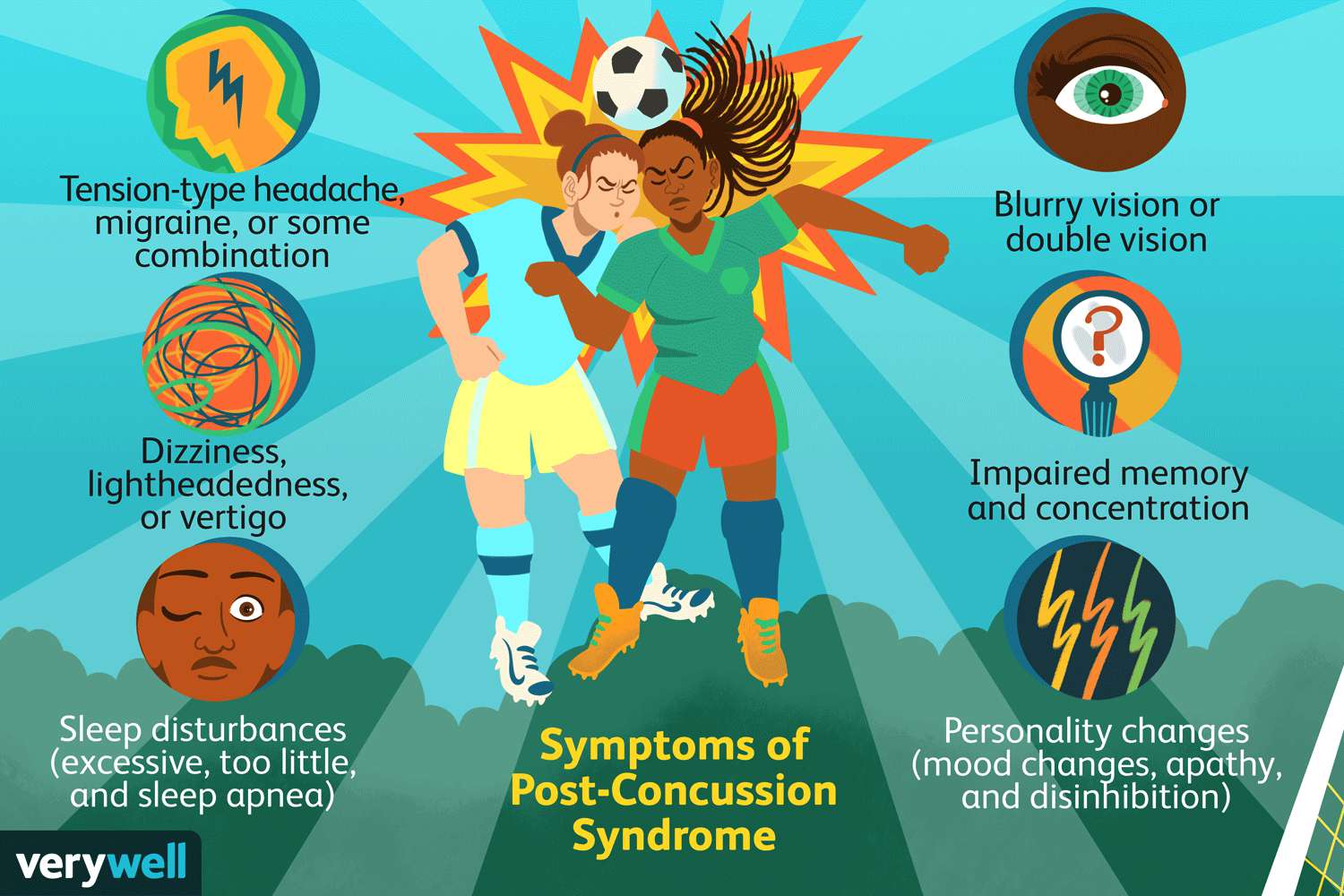
Post-concussion syndrome (PCS) is a collection of symptoms that can occur after a concussion or mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). These symptoms can persist for weeks, months, or even years after the initial injury.
Common Symptoms of Post-Concussion Syndrome
- Physical Symptoms:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Sleep disturbances
- Neck pain
- Cognitive Symptoms:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems
- Slowed thinking
- Trouble with problem-solving
- Emotional Symptoms:
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Mood swings
Risk Factors for Post-Concussion Syndrome
Several factors can increase the risk of developing PCS, including:
- Severity of the Concussion: More severe concussions are more likely to lead to PCS.
- Multiple Concussions: Repeated head injuries can increase the risk of long-term problems.
- Age: Younger and older individuals may be more susceptible to PCS.
- Personal Factors: Individual factors, such as genetics and pre-existing conditions, can influence the severity and duration of symptoms.
Treatment for Post-Concussion Syndrome
While there’s no specific cure for PCS, a multidisciplinary approach can help manage symptoms and promote recovery. Treatment may include:
- Rest: Physical and cognitive rest is essential for healing.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve balance, coordination, and strength.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can help with cognitive and functional tasks, such as memory and problem-solving.
- Medication: Medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms, such as headaches, sleep disturbances, or anxiety.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help individuals develop coping strategies and manage stress.
If you experience symptoms of PCS after a head injury, it’s important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help minimize the long-term impact of the injury.