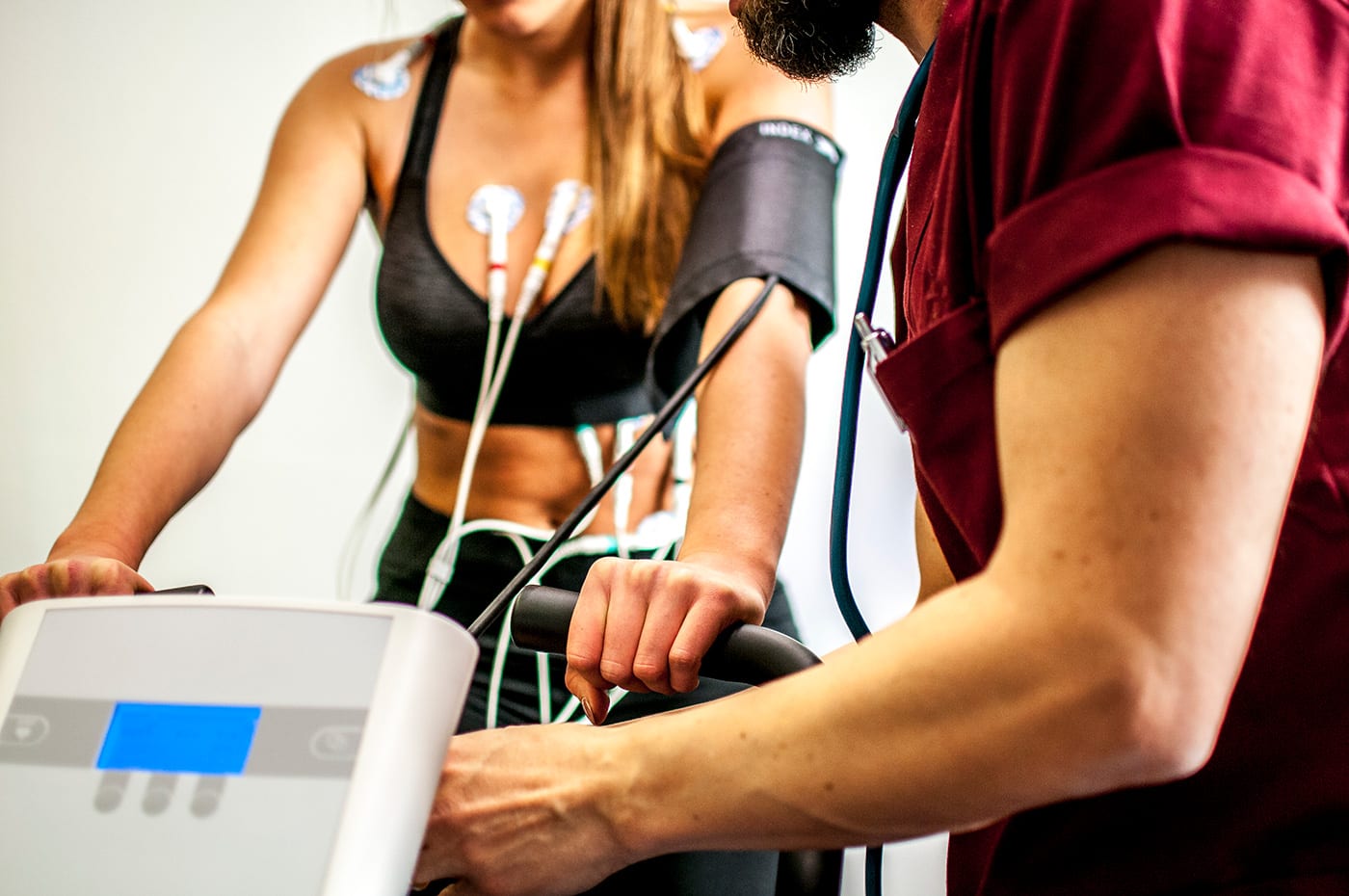
A stress test is a non-invasive procedure used to assess how your heart functions during physical activity or when under stress. It’s often used to diagnose coronary artery disease, which is a condition where plaque buildup narrows the arteries that supply blood to the heart.
Types of Stress Tests
There are several types of stress tests, including:
- Exercise stress test: This involves walking or running on a treadmill or pedaling a stationary bike while your heart rate and blood pressure are monitored.
- Pharmacological stress test: This test uses medication to simulate the effects of exercise on your heart. It’s used for people who cannot exercise due to physical limitations.
- Nuclear stress test: This test uses radioactive tracers to measure blood flow to the heart during exercise and at rest.
- Stress echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to create images of your heart before and after exercise.
What to Expect During a Stress Test
Before the test, you will be asked to avoid caffeine and heavy meals. You may also need to stop taking certain medications. During the test, you will be monitored by a medical professional while you exercise.
Results of a Stress Test
A stress test can help your doctor diagnose coronary artery disease and other heart conditions. It can also help determine the severity of the condition and the best course of treatment. If the test shows that your heart is not receiving enough blood flow during exercise, it may indicate a blockage in one of your coronary arteries.
Risks of a Stress Test
Stress tests are generally safe, but there are some risks involved. These include:
- Chest pain: You may experience chest pain during the test, especially if you have coronary artery disease.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms can occur during or after a stress test.
- Heart attack: In rare cases, a stress test can trigger a heart attack.
If you have symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain or shortness of breath, your doctor may recommend a stress test. It’s a valuable tool for evaluating your heart health and determining the best course of treatment.