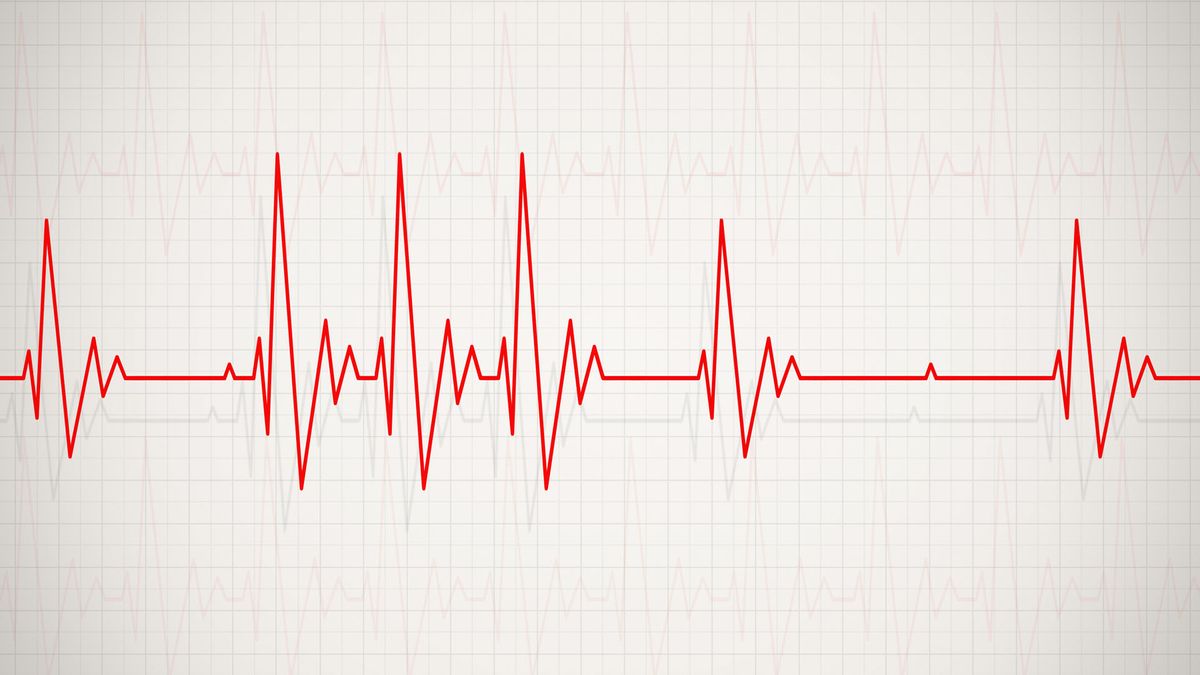
Arrhythmia refers to any abnormal rhythm of the heart. The heart’s electrical signals control its pumping action, and when these signals are disrupted, it can lead to an irregular heartbeat.
Types of Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias can be classified based on their rate and rhythm:
- Bradycardia: A slow heart rate.
- Tachycardia: A fast heart rate.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): A common type of arrhythmia where the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat rapidly and irregularly.
- Atrial Flutter: A rapid, regular heart rhythm in the upper chambers of the heart.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: A rapid heart rate originating in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles).
- Ventricular Fibrillation: A chaotic heart rhythm in the ventricles, which can be life-threatening.
Symptoms of Arrhythmias
The symptoms of arrhythmias can vary depending on the type and severity. Some people may experience no symptoms at all, while others may have:
- Palpitations: A feeling of a racing or fluttering heart.
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting
Causes of Arrhythmias
- Heart Disease: Conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and valve problems can increase the risk of arrhythmias.
- High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure can put stress on the heart and contribute to arrhythmias.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism can affect heart rate.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Low levels of potassium or magnesium can disrupt heart rhythm.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause or worsen arrhythmias.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can trigger arrhythmias in some individuals.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol can affect heart rhythm.
Diagnosis of Arrhythmias
To diagnose an arrhythmia, your doctor may perform the following tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of your heart.
- Holter Monitor: This portable device records your heart’s rhythm for 24 to 48 hours.
- Event Recorder: This device records your heart’s rhythm when you press a button to indicate symptoms.
- Stress Test: This test evaluates your heart’s function during exercise.
Treatment of Arrhythmias
The treatment for arrhythmias depends on the type and severity. It may include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Managing stress, avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol, and getting enough sleep can help prevent arrhythmias.
- Medications: Medications can help control heart rate and rhythm.
- Procedures: In some cases, procedures such as ablation or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) may be necessary to treat arrhythmias.
If you experience symptoms of an arrhythmia, it’s important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications.