Blood clots are a common occurrence in the body, forming to help stop bleeding. However, when blood clots form in the wrong place or at the wrong time, they can be serious health problems.
Types of Blood Clots
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot that forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE): A blood clot that travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow.
- Coronary artery thrombosis: A blood clot that forms in a coronary artery, leading to a heart attack.
- Stroke: A blood clot that forms in a blood vessel in the brain.
Risk Factors for Blood Clots
- Immobility: Prolonged periods of sitting or inactivity can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Surgery: Surgery, especially major surgery, can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Injury: A broken bone or other injury can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as heart disease, cancer, and blood clotting disorders, can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Hormone therapy: Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of blood clots.
Symptoms of Blood Clots
The symptoms of blood clots can vary depending on the location of the clot.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Swelling, pain, and tenderness in the leg, often in the calf.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE): Shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, and lightheadedness.
- Coronary artery thrombosis: Chest pain, shortness of breath, and sweating.
- Stroke: Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body; sudden confusion or trouble understanding; sudden trouble speaking or understanding; sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes; sudden severe headache with no known cause.
Treatment of Blood Clots
The treatment for blood clots depends on the type and severity of the condition. It may include:
- Blood thinners: Medications that help prevent blood clots from forming.
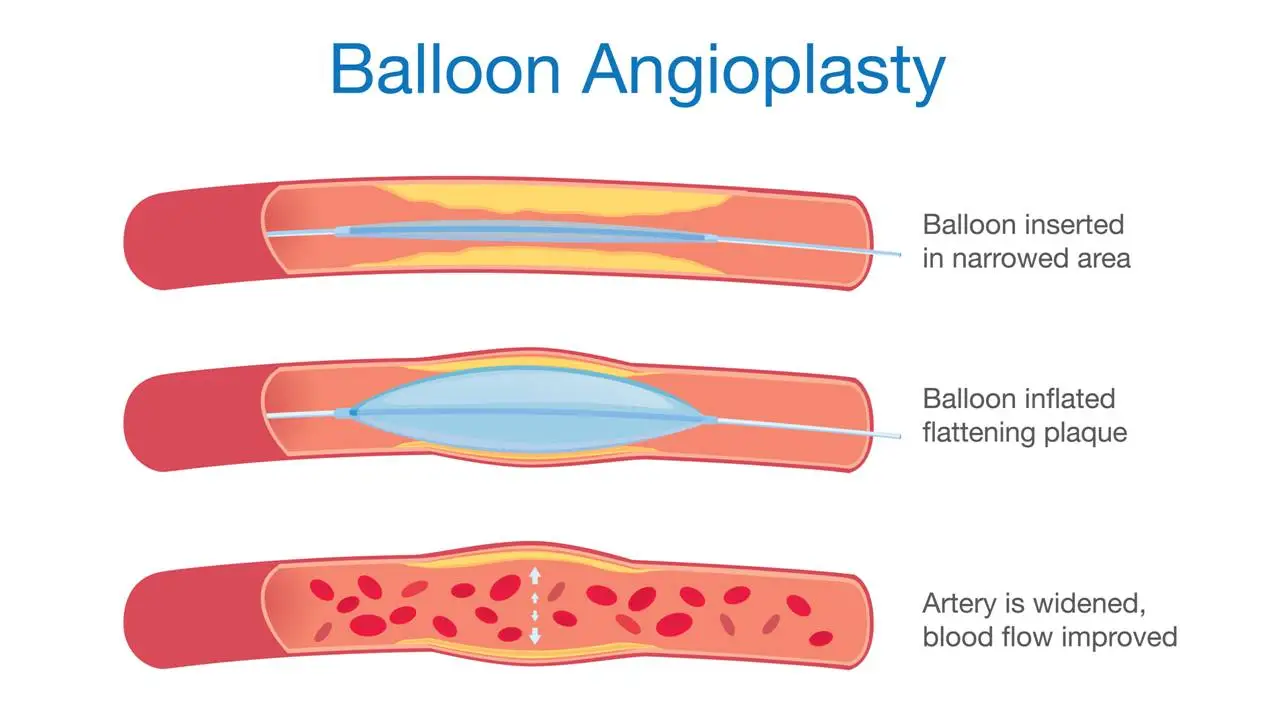
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a blood clot or repair a damaged blood vessel.
Blood clots can be a serious health problem. If you have symptoms of a blood clot, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately.