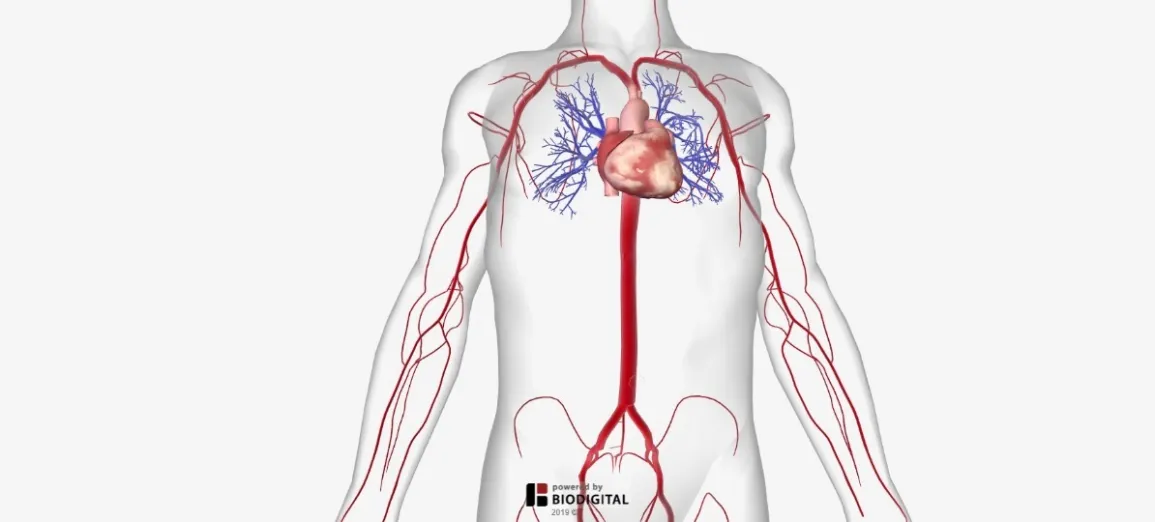
Blood vessels are a vast network of tubes that carry blood throughout the body. They are essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products. There are three main types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
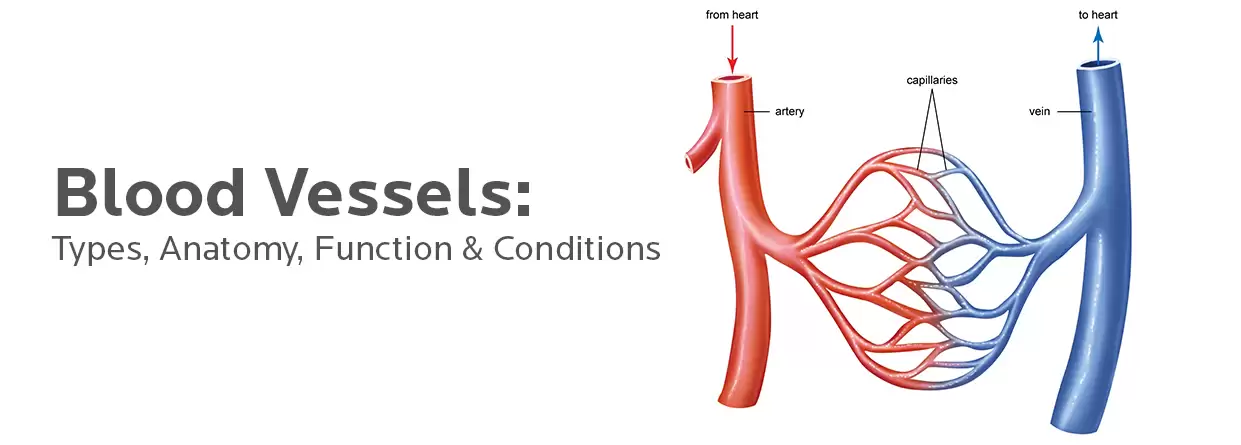
Arteries
Arteries carry blood away from the heart. They are typically thicker and have stronger walls than veins. The largest artery is the aorta, which carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Arteries branch into smaller and smaller vessels, eventually becoming capillaries.
Veins
Veins carry blood back to the heart. They are typically thinner and have less muscular walls than arteries. Veins contain valves that help prevent blood from flowing backward. The largest vein is the superior vena cava, which carries blood from the upper body to the heart, and the inferior vena cava, which carries blood from the lower body to the heart.
Capillaries
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. They connect arteries to veins and allow oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to pass between the blood and the tissues. Capillaries are so thin that red blood cells can only pass through them single file.
Blood Vessel Diseases
A number of diseases can affect the blood vessels. These include:
- Atherosclerosis: A condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to narrowing and reduced blood flow.
- Aneurysm: A bulge in the wall of an artery.
- Varicose veins: Enlarged, twisted veins, often found in the legs.
- Phlebitis: Inflammation of a vein.
Blood vessels are essential for life. Understanding their structure and function can help you maintain healthy blood flow and reduce your risk of blood vessel diseases.