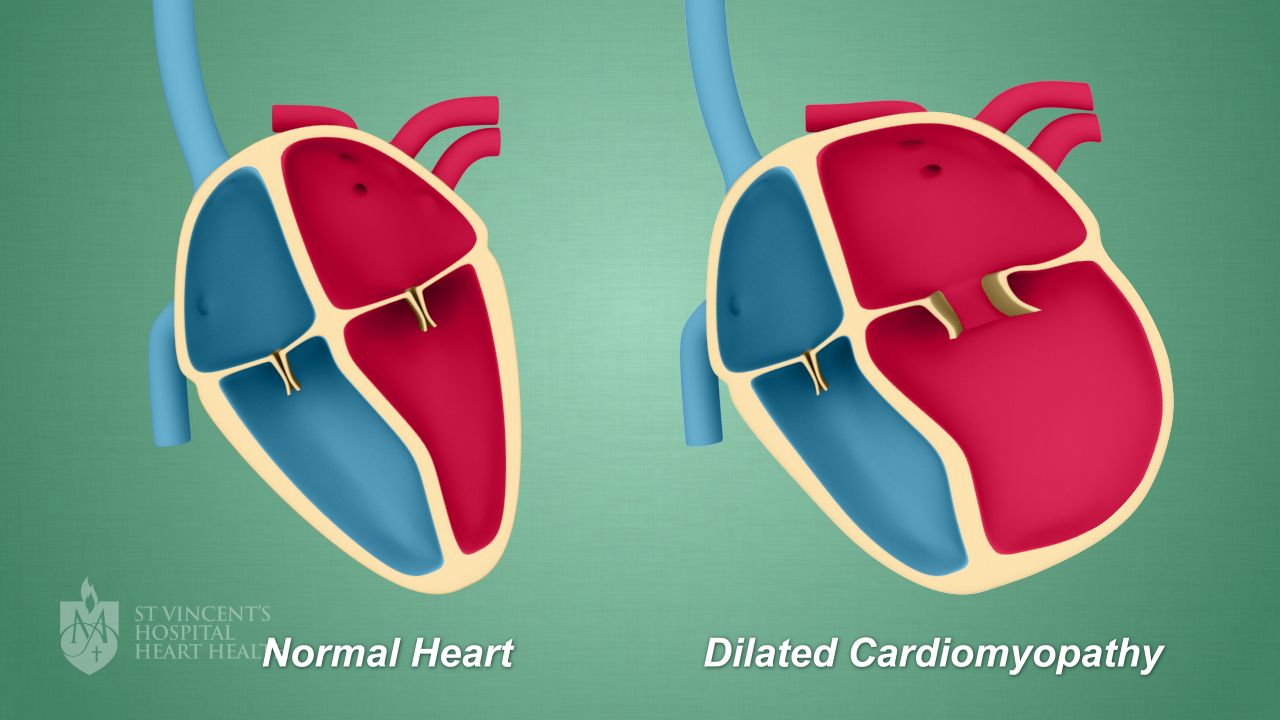
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that can affect its ability to pump blood effectively. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic conditions, infections, and lifestyle factors.
Types of Cardiomyopathy
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: The most common type, characterized by an enlarged heart chamber.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A thickening of the heart muscle, which can make it difficult for the heart to pump blood.
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: A stiffening of the heart muscle, making it difficult for the heart to fill with blood.
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy: A genetic condition that affects the right ventricle of the heart and can lead to arrhythmias.
Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy
The symptoms of cardiomyopathy can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath, especially with activity
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Rapid heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Fainting
Causes of Cardiomyopathy
- Genetic factors: Many types of cardiomyopathy are caused by genetic mutations.
- Infections: Viral infections, such as myocarditis, can damage the heart muscle.
- High blood pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can put stress on the heart and lead to cardiomyopathy.
- Coronary artery disease: Blockages in the heart’s arteries can reduce blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to cardiomyopathy.
- Alcohol abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the heart muscle.
- Certain medications: Some medications can cause cardiomyopathy as a side effect.
Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy
To diagnose cardiomyopathy, your doctor may perform a physical exam and order tests such as:
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
- Chest X-ray: A test that can show if the heart is enlarged.
- Blood tests: To check for signs of heart failure or other underlying conditions.
- Heart biopsy: A procedure to remove a small sample of heart tissue for examination.
Treatment of Cardiomyopathy
The treatment for cardiomyopathy depends on the type and severity of the condition. It may include:
- Medications: Medications can help manage symptoms and improve heart function.
- Implantable devices: Devices such as pacemakers or defibrillators may be implanted to help the heart function properly.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged heart valves or to improve heart function.
- Heart transplantation: In severe cases, a heart transplant may be considered.
Cardiomyopathy is a serious condition that can be managed with proper treatment. If you have symptoms of cardiomyopathy, it’s important to see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.