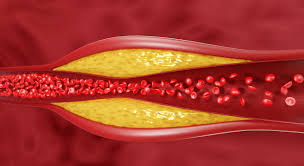
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in all human cells. It plays a vital role in the body, helping to build cell membranes and produce hormones. However, too much cholesterol in the blood can increase the risk of heart disease.
Types of Cholesterol
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, LDL can build up in the arteries and form plaque. High levels of LDL increase the risk of heart disease.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL): Often referred to as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove LDL from the arteries. High levels of HDL can help protect against heart disease.
- Triglycerides: Another type of fat found in the blood. High levels of triglycerides can also increase the risk of heart disease.
Risk Factors for High Cholesterol
- Diet: A diet high in saturated and trans fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of high cholesterol.
- Lack of exercise: Regular physical activity can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and raise HDL cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the arteries and can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes have a higher risk of high cholesterol.
- Family history: A family history of heart disease or high cholesterol can increase your risk.
Symptoms of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol often has no symptoms. However, it can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease and stroke.
Diagnosis of High Cholesterol
A blood test is used to measure cholesterol levels. Your doctor will use this information to assess your risk of heart disease and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment for High Cholesterol
The treatment for high cholesterol often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications.
- Lifestyle changes:
- Healthy diet: A diet low in saturated and trans fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight management: Losing weight if you’re overweight can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the arteries and can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
- Medications: If lifestyle changes alone are not enough to lower your cholesterol, your doctor may prescribe cholesterol-lowering medications.
High cholesterol is a serious health condition that can be managed with appropriate treatment. If you have concerns about your cholesterol levels, it’s important to see your doctor for a checkup.