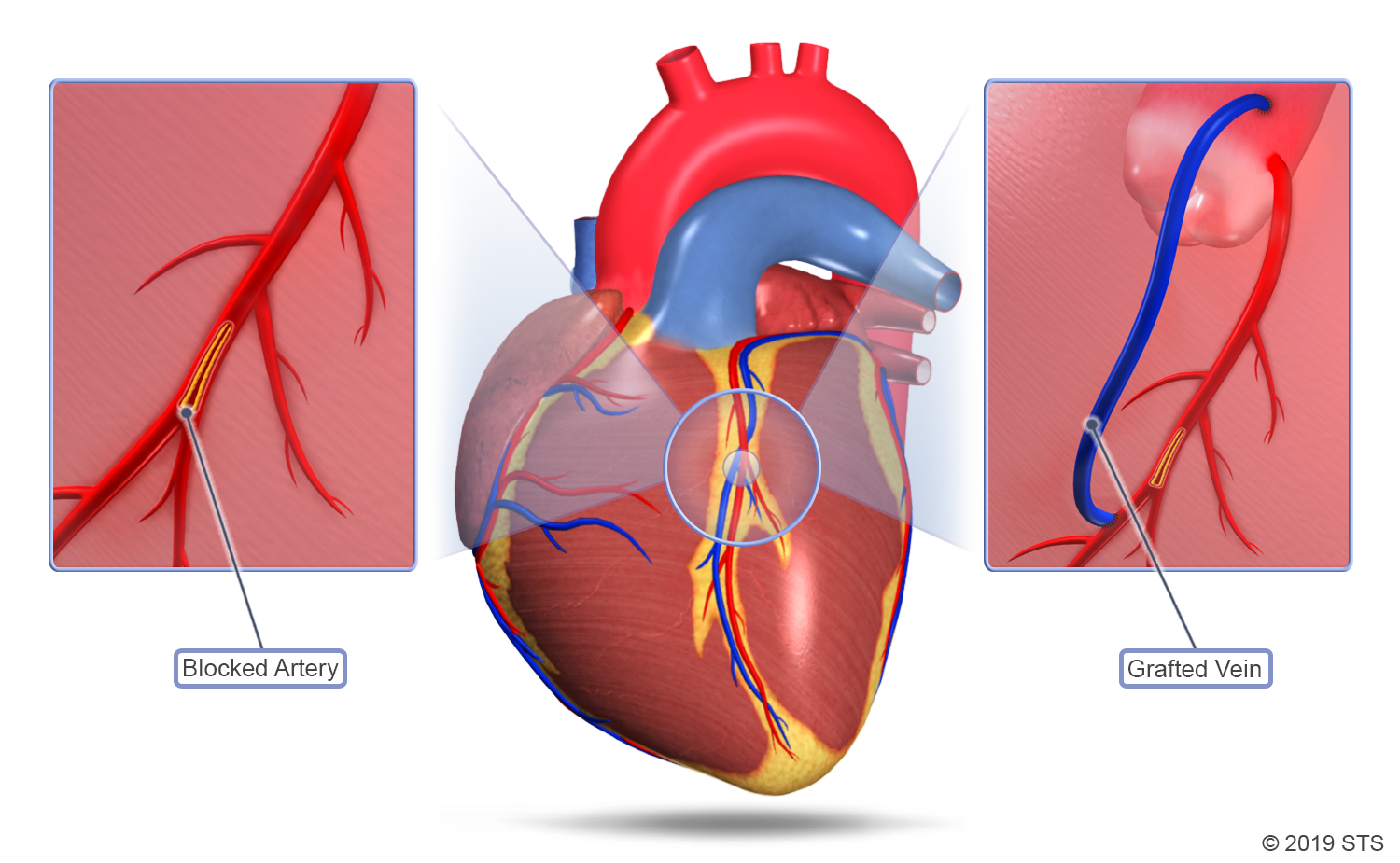
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary artery disease, a condition where plaque buildup narrows the arteries that supply blood to the heart. During CABG, a surgeon reroutes blood around blocked or narrowed arteries, improving blood flow to the heart muscle.
When is CABG Performed?
CABG is typically considered when:
- Medications and lifestyle changes have not been effective in controlling angina (chest pain).
- The coronary arteries are severely narrowed or blocked.
- The patient is at high risk of a heart attack.
The CABG Procedure
- Preparation: The patient undergoes a series of tests, including an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and blood tests, to assess their overall health and determine the best approach for the surgery.
- Anesthesia: The patient is given general anesthesia, which puts them into a deep sleep.
- Incison: The surgeon makes an incision in the chest, either in the middle (sternotomy) or on the side (minimally invasive).
- Harvesting the Graft: The surgeon harvests a healthy artery or vein from another part of the body, typically the leg or chest. This graft will be used to bypass the blocked coronary artery.
- Creating Bypass: The surgeon attaches one end of the graft to the aorta, the main artery leading from the heart. The other end is attached to a coronary artery beyond the blockage. This creates a new pathway for blood to flow to the heart muscle.
- Closure: The incision is closed with stitches or staples.
Recovery from CABG
Recovery from CABG can take several weeks. Patients typically spend a few days in the hospital and may need to undergo rehabilitation to regain strength and stamina.
Risks and Complications
CABG is a major surgical procedure and carries some risks, including:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Kidney failure
- Irregular heart rhythm
However, the benefits of CABG often outweigh the risks for patients with severe coronary artery disease.
If you have coronary artery disease and are considering CABG, it’s important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. They can help you determine if this procedure is right for you.