Depressive disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities.1 These disorders can significantly impact a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
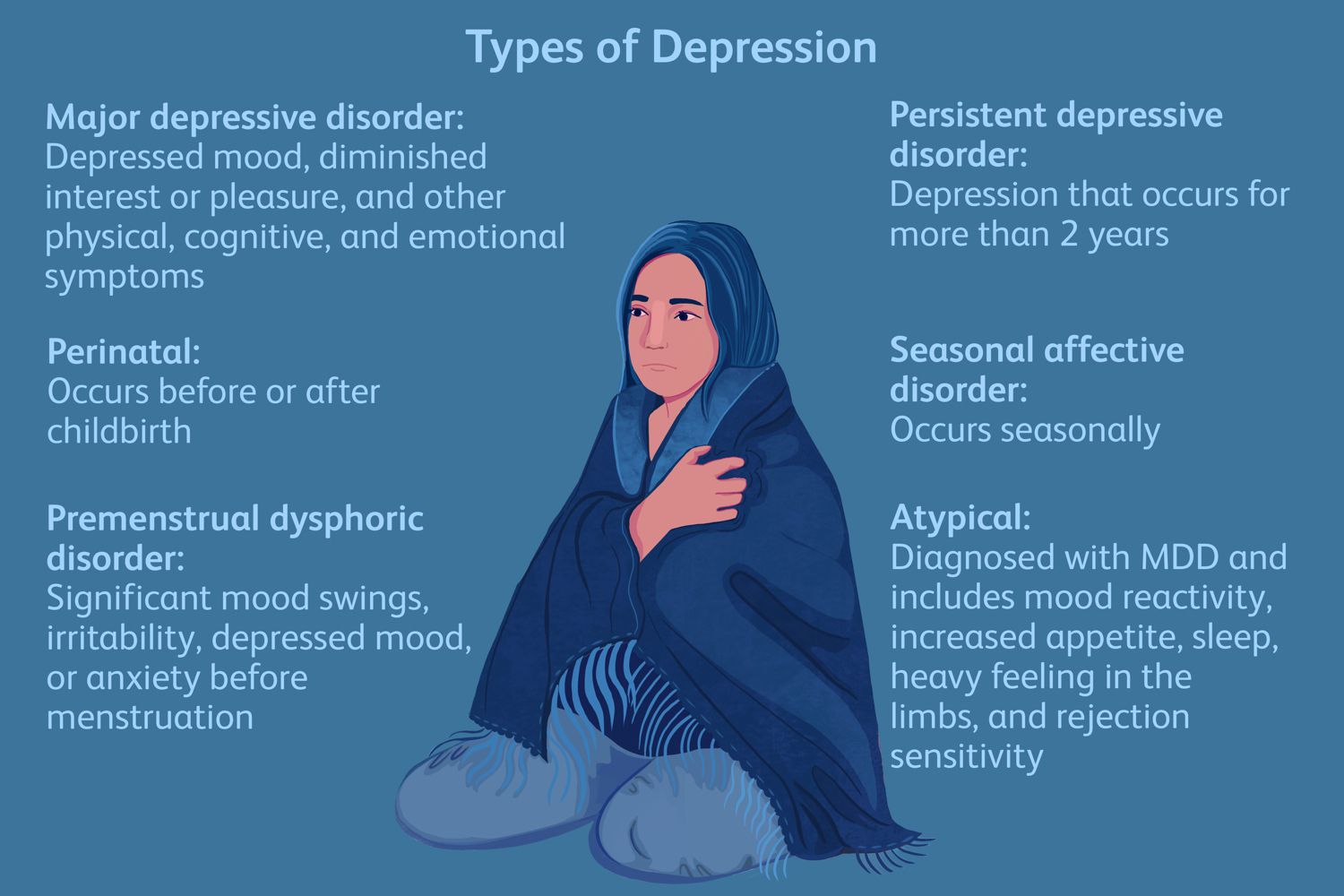
Types of Depressive Disorders
- Major Depressive Disorder: This is a serious mental health condition that causes significant distress and impairment. Symptoms include persistent sadness, feelings of worthlessness, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, and difficulty concentrating.
- Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia): A chronic form of depression that lasts for at least two years. Symptoms are less severe than major depressive disorder but can be persistent.
- Bipolar Disorder: A mental health condition characterized by mood swings, ranging from periods of mania (highs) to depression (lows).
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): A type of depression that occurs during certain seasons, typically winter, when there is less sunlight.
Symptoms of Depressive Disorders
Symptoms of depressive disorders can vary, but may include:
- Persistent sadness or emptiness
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Sleep disturbances
- Fatigue or loss of2 energy
- Difficulty concentrating
- Feelings of worthlessness or guilt3
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Causes of Depressive Disorders
The exact causes of depressive disorders are not fully understood, but a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors may contribute to their development. Some potential causes include:
- Genetics: A family history of depression may increase the risk.
- Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, may play a role.
- Life Events: Stressful life events, such as loss or trauma, can trigger depressive episodes.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or chronic pain, can contribute to depression.
Treatment of Depressive Disorders
Treatment for depressive disorders often involves a combination of therapy and medication.
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and behaviors.
- Medication: Antidepressants can help regulate mood and alleviate symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep can improve mood and overall well-being.
If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, it’s important to seek professional help. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life.