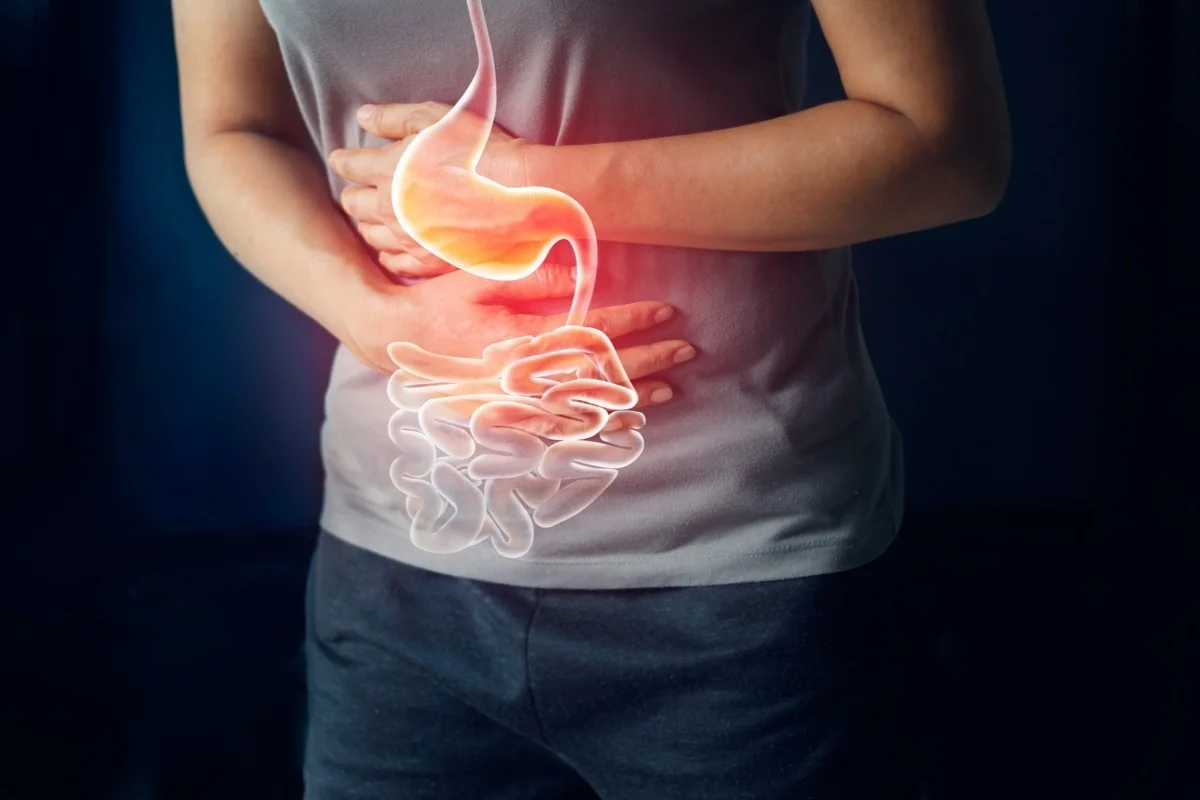
Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders affect the digestive tract, which includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. These disorders can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain and complications.
Common Gastrointestinal Disorders:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic condition that affects the large intestine, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A group of inflammatory bowel diseases, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, that cause inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A condition in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and other symptoms.1
- Peptic Ulcer Disease:2 Open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or small intestine.
- Diverticular Disease: Small pouches or sacs that bulge outward from the colon wall.
- Constipation: Difficulty or infrequent bowel movements.
- Diarrhea: Loose, watery stools.
- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Symptoms of Gastrointestinal Disorders
Symptoms can vary depending on the specific disorder, but may include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation)
- Bloating and gas
- Nausea and vomiting
- Heartburn
- Indigestion
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss or gain
- Fatigue
- Rectal bleeding
Treatment and Management
Treatment for GI disorders depends on the specific condition and its severity. Common treatment approaches include:
- Dietary Changes: Modifying your diet can help manage symptoms, such as avoiding trigger foods or following a specific diet, like the low-FODMAP diet.
- Medication: Medications can help to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and heal damaged tissues.
- Lifestyle Changes: Stress management, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can improve overall digestive health.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat severe conditions or complications.
If you are experiencing persistent GI symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help improve your quality of life and prevent complications.